Introduction to Hand Surgery
Human hand is a masterpiece of evolution. Use of upper limbs with opposable thumbs for tool making and handling has contributed immensely for humanity to evolve as a dominant species on the earth. Amongst many evolving medical super-specialities, field of hand surgery treats hand as a specialised organ rather than compartmentalising it among bone [orthopaedic], soft tissue coverage (plastic surgery (vascular injuries (vascular surgery), etc. Many developed countries like Singapore, Finland, Sweden have separate training programms for hand surgery independent of other specialities. India has started with Fellowship of National Board and recently M. Ch. programmes in hand surgery.
Broadly, one may look at the practice of hand surgery in 2 parts- paediatric and adult patients. Congenital hand differences in children are a source of immense distress and worry to the parents. Common nontraumatic problems of hand in this age group are syndactyly, radial club hand, absence of thumb, spastic hand in association with cerebral palsy, brachial plexus birth palsy, etc. Appropriate intervention at an appropriate time is crucial for near-normal development of growing hands. [Fig. 1 & 2]
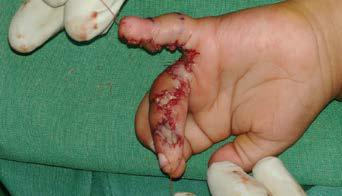
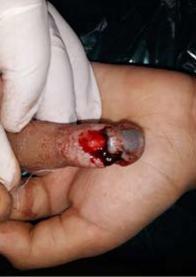
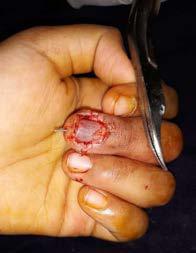
Children in their curious exploration of surroundings sometimes do get injured. A common scenario is fingertip crush injuries due to window sills and doors. Repairs of such injuries can produce very gratifying results. [Fig. 3 & 4]